Modelscope Swift
SwanLab已经与Swift官方集成,见:#3142
可视化在线Demo:swift-robot
Modelscope魔搭社区 的 Swift 是一个集模型训练、微调、推理、部署于一体的框架。

🍲 ms-swift 是 ModelScope 社区提供的官方框架,用于微调和部署大型语言模型和多模态大型模型。它目前支持 450+ 大型模型和 150+ 多模态大型模型的训练(预训练、微调、人工对齐)、推理、评估、量化和部署。
🍔 此外,ms-swift 还采用了最新的训练技术,包括 LoRA、QLoRA、Llama-Pro、LongLoRA、GaLore、Q-GaLore、LoRA+、LISA、DoRA、FourierFt、ReFT、UnSloth 和 Liger 等轻量级技术,以及 DPO、GRPO、RM、PPO、KTO、CPO、SimPO 和 ORPO 等人工对齐训练方法。
ms-swift 支持使用 vLLM 和 LMDeploy 加速推理、评估和部署模块,并支持使用 GPTQ、AWQ 和 BNB 等技术进行模型量化。此外,ms-swift 还提供了基于 Gradio 的 Web UI 和丰富的最佳实践。
你可以使用Swift快速进行模型训练,同时使用SwanLab进行实验跟踪与可视化。
0. 安装ms-swift和swanlab
安装ms-swift(>=3.1.1):
pip install ms-swift安装swanlab:
pip install swanlab1. CLI微调
你只需要在ms-swift的CLI中添加--report_to和--swanlab_project两个参数,即可使用SwanLab进行实验跟踪与可视化:
swift sft \
...
--report_to swanlab \
--swanlab_project swift-robot \
...下面是在swift官方的CLI微调案例,中结合SwanLab的示例(见代码最后):
# 22GB
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 \
swift sft \
--model Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct \
--train_type lora \
--dataset 'AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-zh#500' \
'AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-en#500' \
'swift/self-cognition#500' \
--torch_dtype bfloat16 \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 1 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 1 \
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
--lora_rank 8 \
--lora_alpha 32 \
--target_modules all-linear \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 16 \
--eval_steps 50 \
--save_steps 50 \
--save_total_limit 5 \
--logging_steps 5 \
--max_length 2048 \
--output_dir output \
--system 'You are a helpful assistant.' \
--warmup_ratio 0.05 \
--dataloader_num_workers 4 \
--model_author swift \
--model_name swift-robot \
--report_to swanlab \
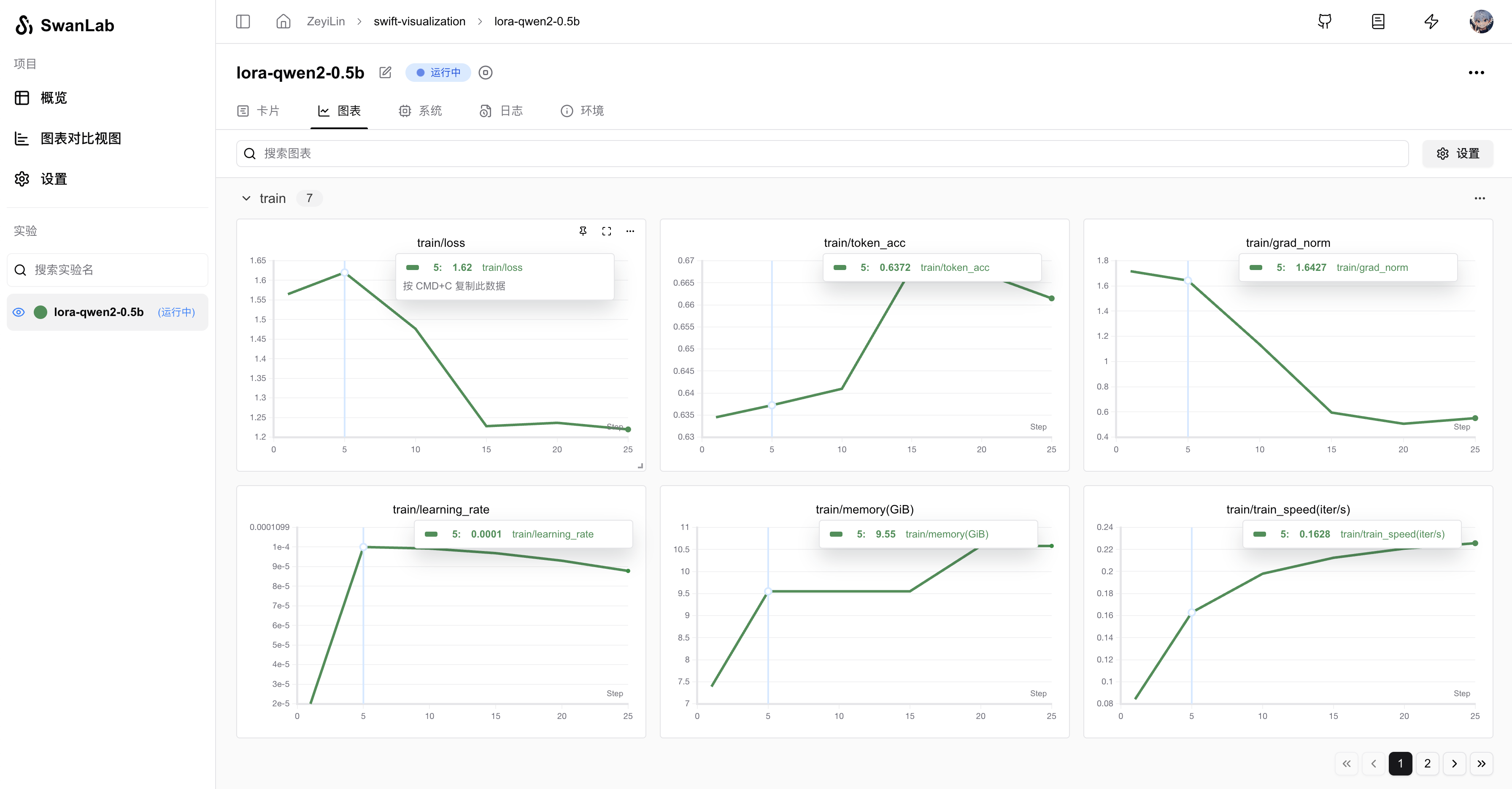
--swanlab_project swift-robot运行指令后,就可以在SwanLab看到训练过程:
支持的完整参数:
swanlab_token: SwanLab的api-keyswanlab_project: swanlab的projectswanlab_workspace: 默认为None,会使用api-key对应的usernameswanlab_exp_name: 实验名,可以为空,为空时默认传入--output_dir的值swanlab_mode: 可选cloud和local,云模式或者本地模式
2. WebUI微调
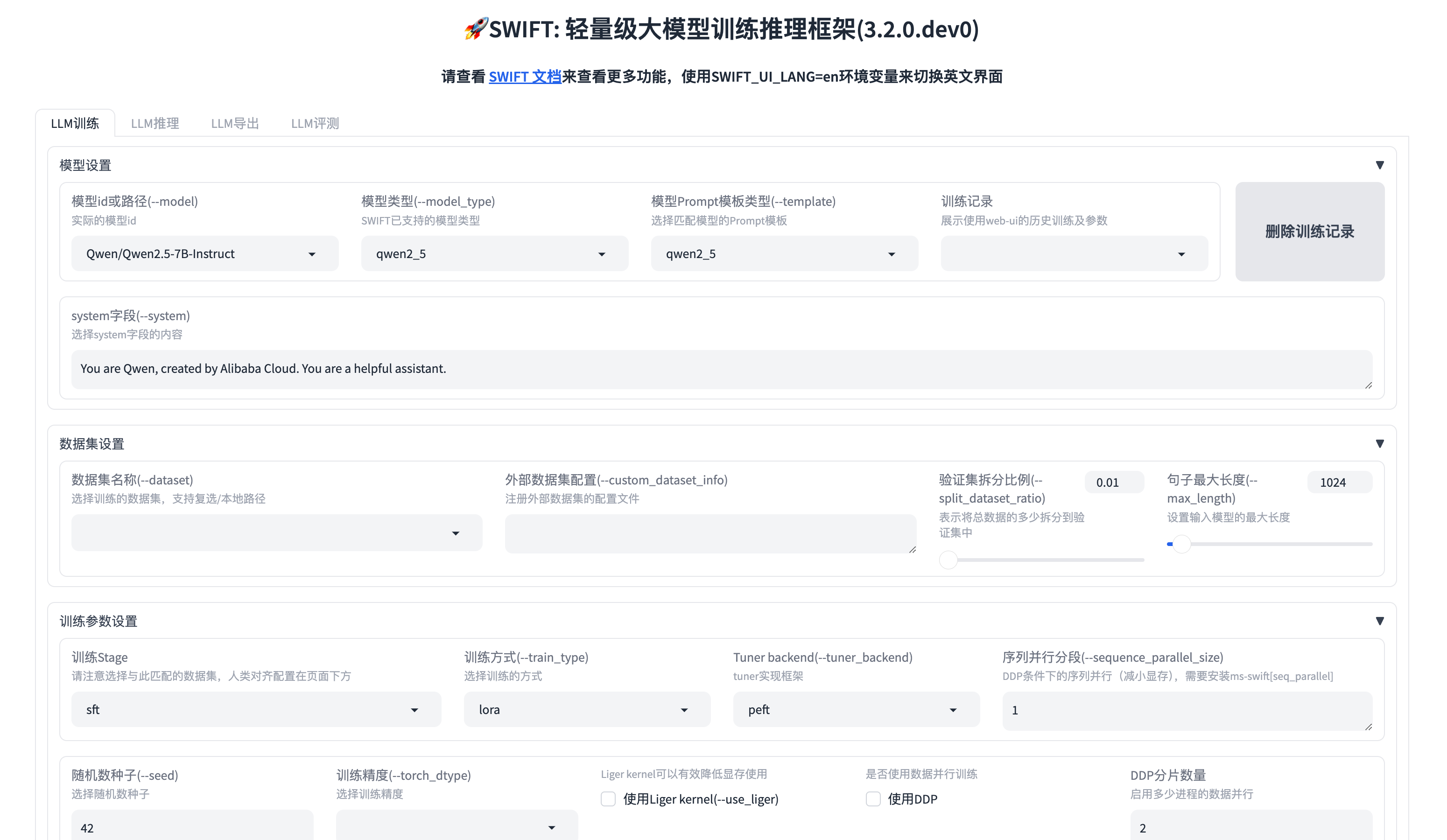
Swift不仅支持CLI微调,还为开发者提供非常方便的**WebUI(网页端)**的微调界面。你同样可以在WebUI当中启动SwanLab跟踪实验。
启动WebUI方式:
swift web-ui启动后,会自动打开浏览器,显示微调界面(或者访问 http://localhost:7860/ ):
在下方的「训练记录」模块中,在训练记录方式部分选择swanlab:
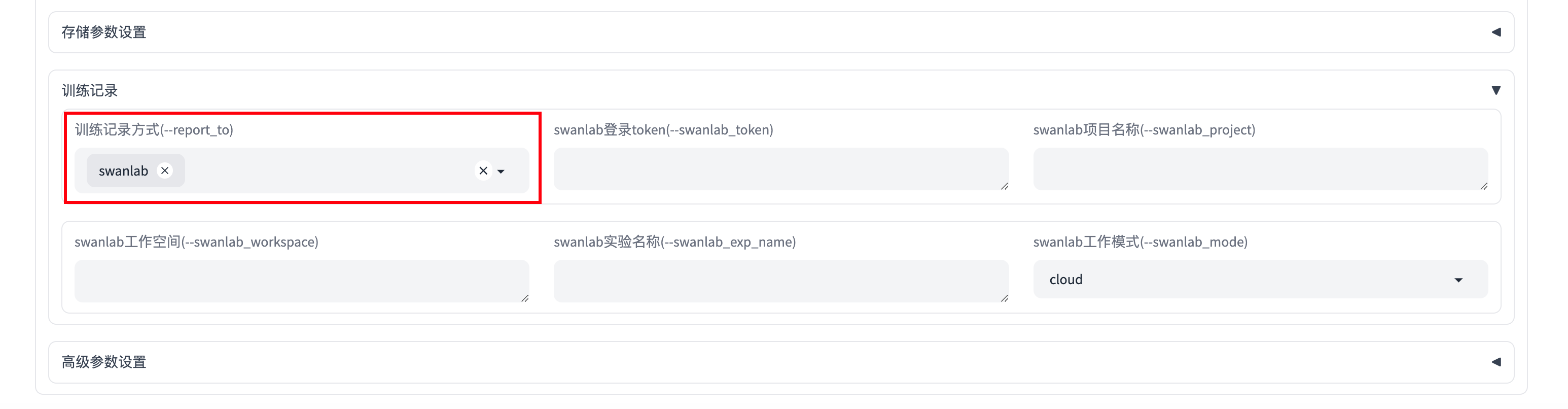
你还可以在「训练记录」模块的其他填写更细致的swanlab参数,包括:
swanlab_token: SwanLab的api-keyswanlab_project: swanlab的projectswanlab_workspace: 默认为None,会使用api-key对应的usernameswanlab_exp_name: 实验名,可以为空,为空时默认传入--output_dir的值swanlab_mode: 可选cloud和local,云模式或者本地模式
然后,点击「🚀开始训练」按钮,即可启动训练,并使用SwanLab跟踪实验:
3. Python代码微调
3.1 引入SwanLabCallback
因为Swift的trainer集成自transformers,所以可以直接使用swanlab与huggingface集成的SwanLabCallback:
from swanlab.integration.transformers import SwanLabCallbackSwanLabCallback可以定义的参数有:
- project、experiment_name、description 等与 swanlab.init 效果一致的参数, 用于SwanLab项目的初始化。 你也可以在外部通过swanlab.init创建项目,集成会将实验记录到你在外部创建的项目中。
3.2 引入Trainer
from swanlab.integration.transformers import SwanLabCallback
from swift import Seq2SeqTrainer, Seq2SeqTrainingArguments
···
#实例化SwanLabCallback
swanlab_callback = SwanLabCallback(project="swift-visualization")
trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer(
...
callbacks=[swanlab_callback],
)
trainer.train()3.3 使用SwanLabCallback
Lora微调一个Qwen2-0.5B模型
from swanlab.integration.transformers import SwanLabCallback
from swift import Seq2SeqTrainer, Seq2SeqTrainingArguments
from swift.llm import get_model_tokenizer, load_dataset, get_template, EncodePreprocessor
from swift.utils import get_logger, find_all_linears, get_model_parameter_info, plot_images, seed_everything
from swift.tuners import Swift, LoraConfig
from swift.trainers import Seq2SeqTrainer, Seq2SeqTrainingArguments
from functools import partial
import os
logger = get_logger()
seed_everything(42)
# Hyperparameters for training
# model
model_id_or_path = 'Qwen/Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct' # model_id or model_path
system = 'You are a helpful assistant.'
output_dir = 'output'
# dataset
dataset = ['AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-zh#500', 'AI-ModelScope/alpaca-gpt4-data-en#500',
'swift/self-cognition#500'] # dataset_id or dataset_path
data_seed = 42
max_length = 2048
split_dataset_ratio = 0.01 # Split validation set
num_proc = 4 # The number of processes for data loading.
# The following two parameters are used to override the placeholders in the self-cognition dataset.
model_name = ['小黄', 'Xiao Huang'] # The Chinese name and English name of the model
model_author = ['魔搭', 'ModelScope'] # The Chinese name and English name of the model author
# lora
lora_rank = 8
lora_alpha = 32
# training_args
training_args = Seq2SeqTrainingArguments(
output_dir=output_dir,
learning_rate=1e-4,
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
per_device_eval_batch_size=1,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
weight_decay=0.1,
lr_scheduler_type='cosine',
warmup_ratio=0.05,
logging_first_step=True,
save_strategy='steps',
save_steps=50,
eval_strategy='steps',
eval_steps=50,
gradient_accumulation_steps=16,
num_train_epochs=1,
metric_for_best_model='loss',
save_total_limit=5,
logging_steps=5,
dataloader_num_workers=1,
data_seed=data_seed,
)
output_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.expanduser(output_dir))
logger.info(f'output_dir: {output_dir}')
# Obtain the model and template, and add a trainable Lora layer on the model.
model, tokenizer = get_model_tokenizer(model_id_or_path)
logger.info(f'model_info: {model.model_info}')
template = get_template(model.model_meta.template, tokenizer, default_system=system, max_length=max_length)
template.set_mode('train')
target_modules = find_all_linears(model)
lora_config = LoraConfig(task_type='CAUSAL_LM', r=lora_rank, lora_alpha=lora_alpha,
target_modules=target_modules)
model = Swift.prepare_model(model, lora_config)
logger.info(f'lora_config: {lora_config}')
# Print model structure and trainable parameters.
logger.info(f'model: {model}')
model_parameter_info = get_model_parameter_info(model)
logger.info(f'model_parameter_info: {model_parameter_info}')
# Download and load the dataset, split it into a training set and a validation set,
# and encode the text data into tokens.
train_dataset, val_dataset = load_dataset(dataset, split_dataset_ratio=split_dataset_ratio, num_proc=num_proc,
model_name=model_name, model_author=model_author, seed=data_seed)
logger.info(f'train_dataset: {train_dataset}')
logger.info(f'val_dataset: {val_dataset}')
logger.info(f'train_dataset[0]: {train_dataset[0]}')
train_dataset = EncodePreprocessor(template=template)(train_dataset, num_proc=num_proc)
val_dataset = EncodePreprocessor(template=template)(val_dataset, num_proc=num_proc)
logger.info(f'encoded_train_dataset[0]: {train_dataset[0]}')
# Print a sample
template.print_inputs(train_dataset[0])
# Get the trainer and start the training.
model.enable_input_require_grads() # Compatible with gradient checkpointing
swanlab_callback = SwanLabCallback(
project="swift-visualization",
experiment_name="lora-qwen2-0.5b",
description="Lora微调一个Qwen2-0.5B模型"
)
trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
data_collator=template.data_collator,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=val_dataset,
template=template,
callbacks=[swanlab_callback],
)
trainer.train()
last_model_checkpoint = trainer.state.last_model_checkpoint
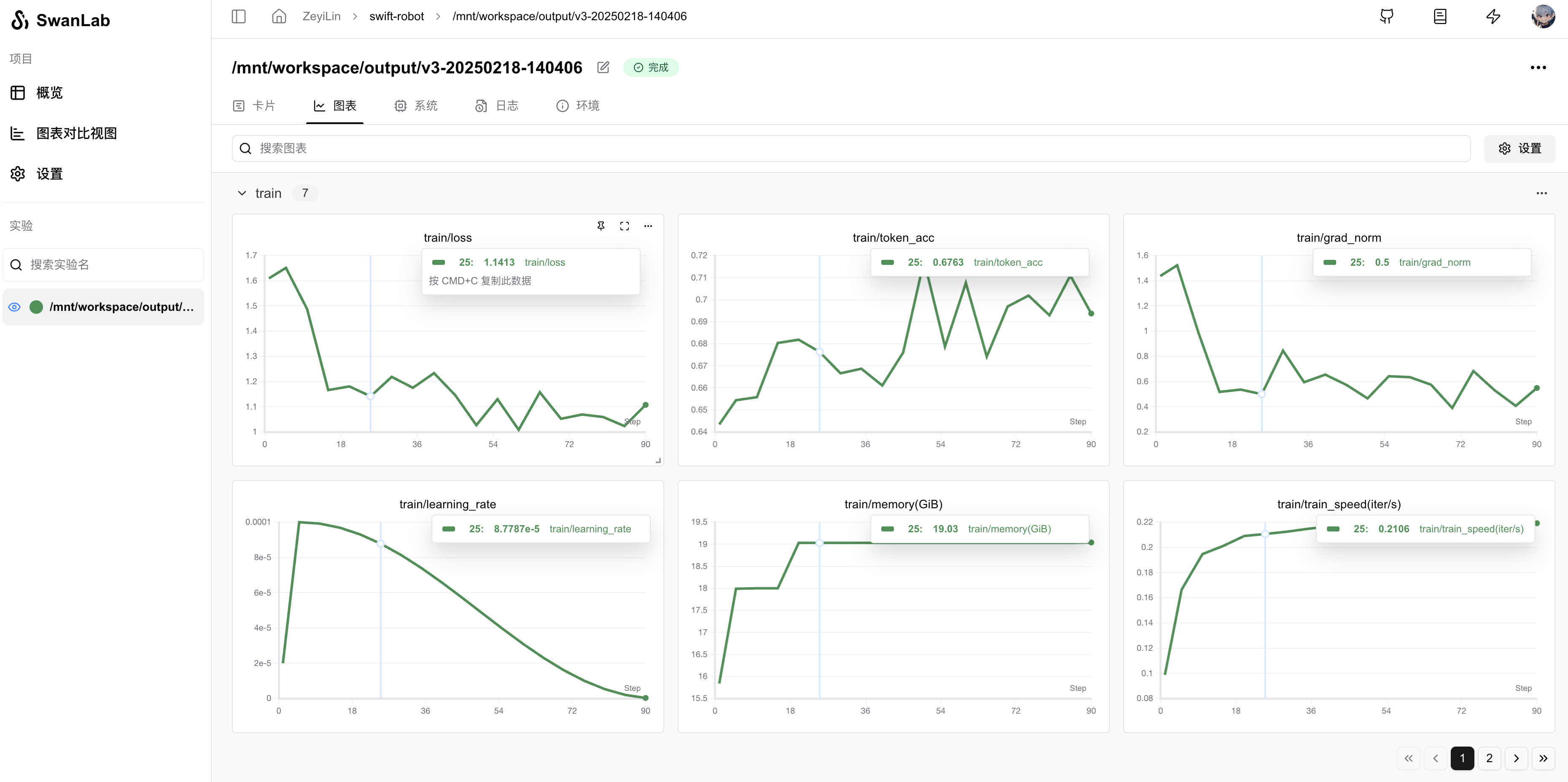
logger.info(f'last_model_checkpoint: {last_model_checkpoint}')运行可视化结果: