FAQ
Why can't I input the API Key during login?
Refer to this answer: Link
How to start multiple experiments from a single script?
Add swanlab.finish() between multiple experiment creations.
After executing swanlab.finish(), executing swanlab.init() again will create a new experiment.
If swanlab.finish() is not executed, subsequent swanlab.init() calls will be ignored.
How to Upload Data to a Self-Hosted SwanLab?
There are two ways to achieve this:
swanlab.login(api_key='Your API Key', host='Your Self-Hosted Server Address')swanlab login --host Your_Self-Hosted_Server_Address --api-key Your_API_KeyAfter logging in, you can specify the data to be uploaded to your self-hosted SwanLab.
How to disable SwanLab logging during training (for debugging)?
Set the mode parameter of swanlab.init to 'disabled' to prevent experiment creation and data logging.
swanlab.init(mode='disabled')The local training has ended, but the experiment is still shown as running on the SwanLab UI. How to change the status?
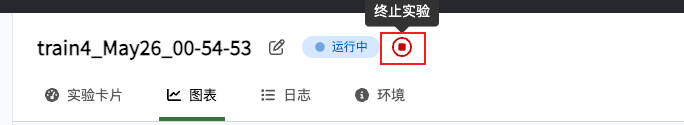
Click the stop button next to the experiment name to change the status from "Running" to "Interrupted" and stop receiving data uploads.
On the same machine, multiple people are using SwanLab. How should it be configured?
After completing the login with swanlab.login, a configuration file will be generated on the machine to record the login information, so that there is no need to log in again next time. However, if multiple people are using the same machine, care must be taken to avoid logs being transmitted to someone else's account.
There are two recommended configuration methods:
Method 1: Add swanlab.login(api_key='Your API Key') at the beginning of the code.
Method 2: Before running the code, set the environment variable SWANLAB_API_KEY="Your API Key".
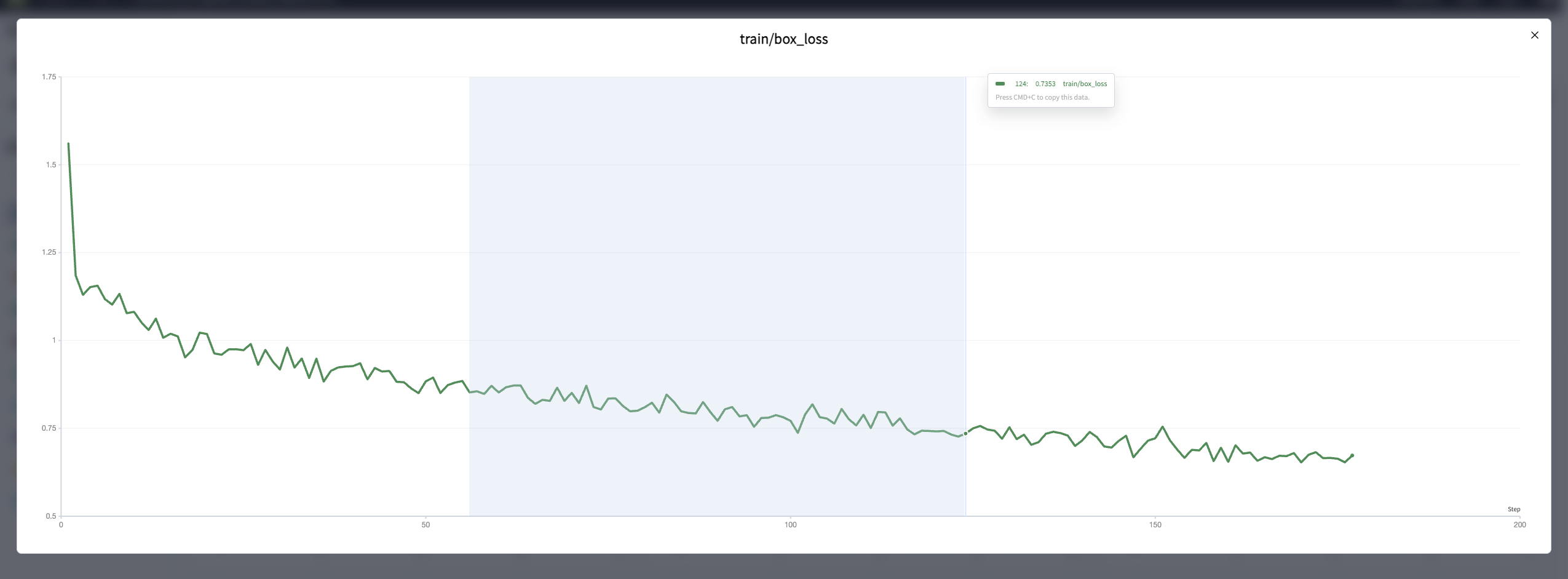
How to view local details of the line chart?
Zoom in on the line chart by holding down the mouse and dragging over the target area to magnify that region.
Internal Metric Names
Metric names refer to the key part of the dictionary passed into swanlab.log(). Some keys are internally used by SwanLab to transmit system hardware metrics, so it is not recommended to use them.
Internal metrics include:
__swanlab__.xxx
Experiment Status Rules
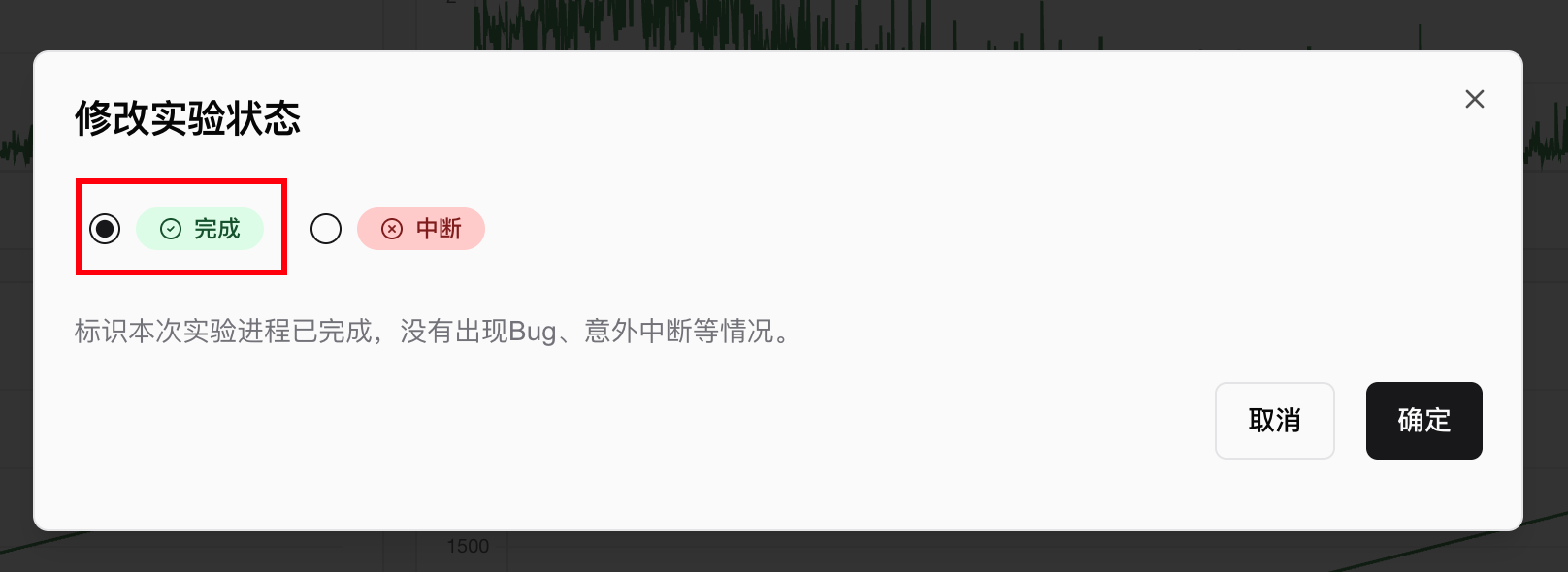
An experiment can be in one of three states: Completed, Running, or Crashed.
- Completed: The training process has ended naturally, or
swanlab.finish()was manually executed. - Running: The training process is ongoing, and
swanlab.finish()has not been executed. - Crashed: The training process was abnormally terminated due to bugs, machine shutdown,
Ctrl+C, etc.
Some users may encounter the following situation: Why does my training process seem to be ongoing, but the SwanLab chart shows it as crashed?
This is because SwanLab has a hidden rule for determining crashes. If no logs (including automatically collected system metrics) are uploaded within 30 minutes, the experiment is marked as crashed. This is to prevent the experiment from remaining in the "Running" state indefinitely if the training process is unexpectedly killed and cannot trigger the status upload logic in the SwanLab SDK.
Therefore, if your machine experiences network issues for more than 30 minutes, the experiment status will be displayed as "Crashed."
Command Line Logging and Truncation
SwanLab records the standard output stream in the process after swanlab.init(), which can be viewed in the "Logs" tab of the experiment. If a line of command-line output is too long, it will be truncated. The current default limit is 1024 characters, and the maximum limit is 4096 characters.
If you want to modify the limit, you can use the following code to adjust it:
import swanlab
# Create a new settings object and modify the max_log_length parameter
new_settings = swanlab.Settings(
max_log_length=4096,
)
# Update global settings
swanlab.merge_settings(new_settings)
swanlab.init()
...How to enable experiment smoothing
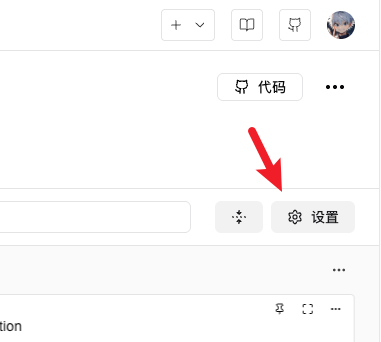
Find the "Settings" button in the upper right corner of the experiment page and click it:
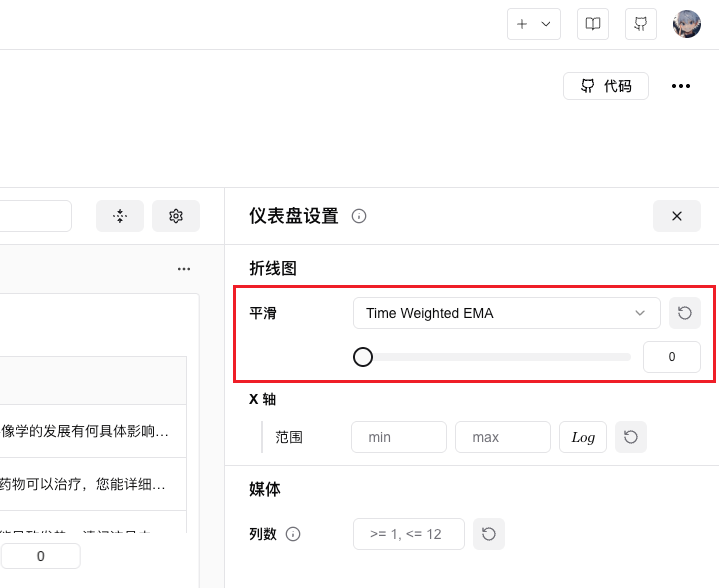
In the menu pulled out on the right, find the "Smooth" option and slide the slider to enable smoothing:
How to Change an Experiment's 'Crashed' Status
On the experiment page, click the status label:
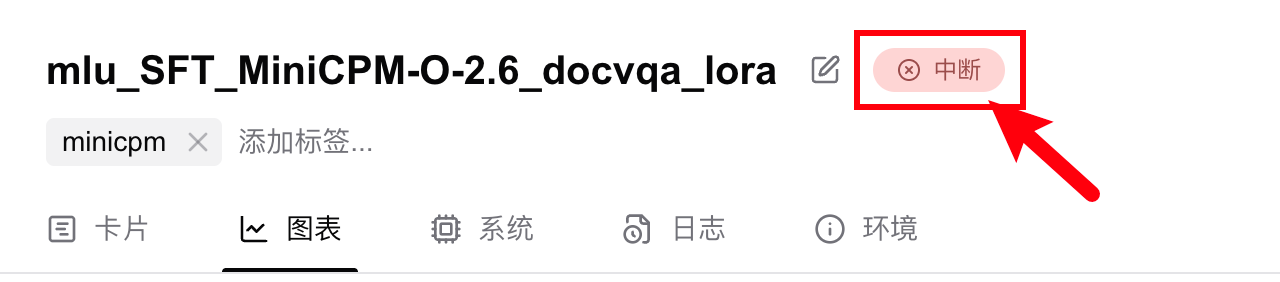
In the pop-up window, select your desired status:
How to enable resume training?
Refer to the documentation: resume
How to disable system hardware monitoring?
swanlab.init(
settings=swanlab.Settings(
hardware_monitor=False,
)
)