MNIST Handwritten Digit Recognition
INFO
Image Classification, Machine Learning Introduction, Grayscale Images
Overview
MNIST handwritten digit recognition is one of the most classic introductory tasks in deep learning, proposed by LeCun et al.
This task is based on the MNIST dataset, where researchers build machine learning models to recognize 10 handwritten digits (0-9).

This case study primarily focuses on:
- Using
pytorchto build, train, and evaluate a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network). - Using
swanlabto track hyperparameters, record metrics, and visualize monitoring throughout the training cycle.
Environment Setup
This case study is based on Python>=3.8. Please ensure Python is installed on your computer.
Environment dependencies:
torch
torchvision
swanlabQuick installation command:
bash
pip install torch torchvision swanlabComplete Code
python
import os
import torch
from torch import nn, optim, utils
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
import swanlab
# CNN network construction
class ConvNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 1,28x28
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, 5) # 10, 24x24
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, 3) # 128, 10x10
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(20 * 10 * 10, 500)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(500, 10)
def forward(self, x):
in_size = x.size(0)
out = self.conv1(x) # 24
out = F.relu(out)
out = F.max_pool2d(out, 2, 2) # 12
out = self.conv2(out) # 10
out = F.relu(out)
out = out.view(in_size, -1)
out = self.fc1(out)
out = F.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
out = F.log_softmax(out, dim=1)
return out
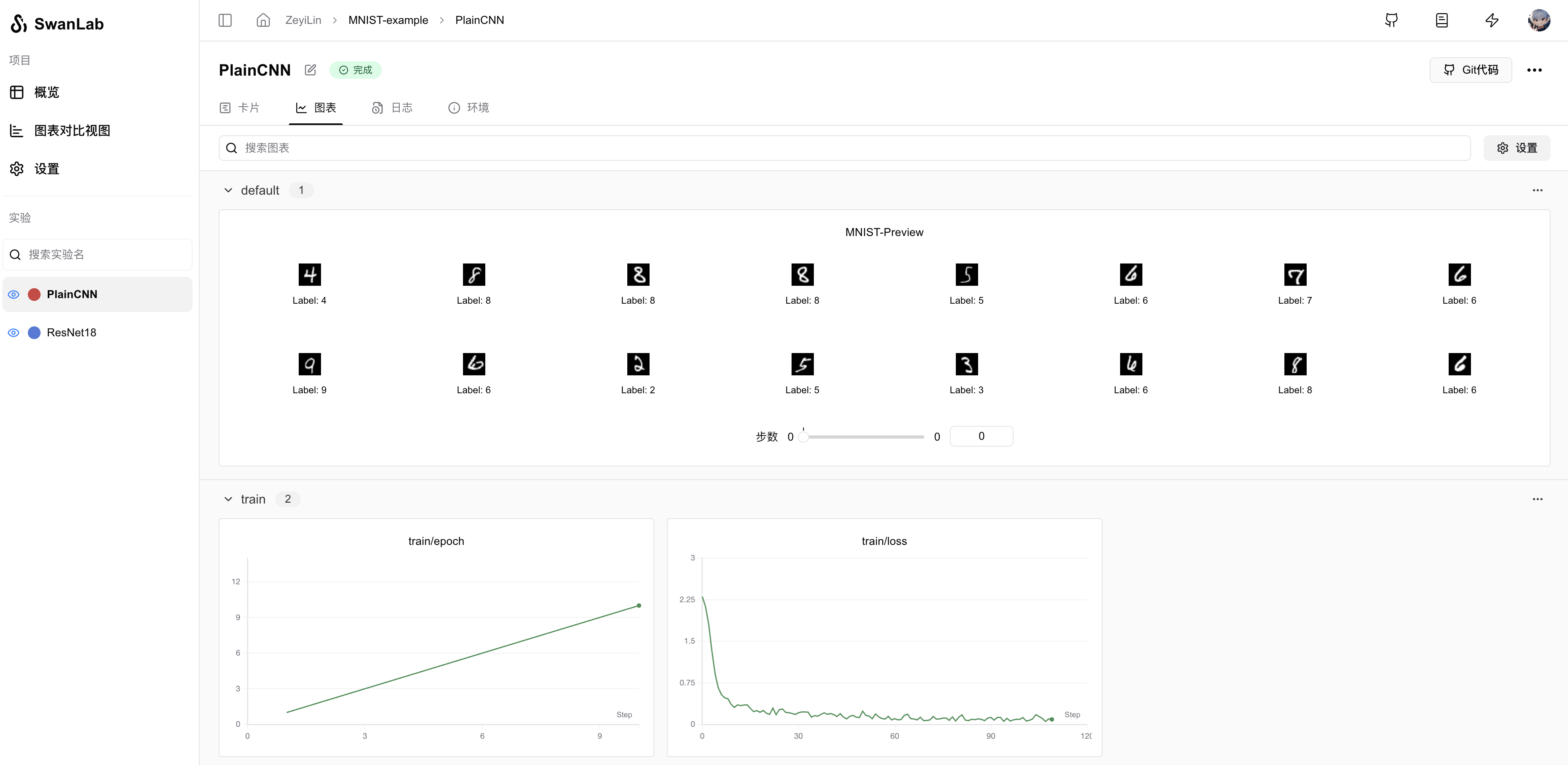
# Capture and visualize the first 20 images
def log_images(loader, num_images=16):
images_logged = 0
logged_images = []
for images, labels in loader:
# images: batch of images, labels: batch of labels
for i in range(images.shape[0]):
if images_logged < num_images:
# Use swanlab.Image to convert images to wandb visualization format
logged_images.append(swanlab.Image(images[i], caption=f"Label: {labels[i]}"))
images_logged += 1
else:
break
if images_logged >= num_images:
break
swanlab.log({"MNIST-Preview": logged_images})
def train(model, device, train_dataloader, optimizer, criterion, epoch, num_epochs):
model.train()
# 1. Loop through train_dataloader, fetching images and labels in batches
for iter, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(train_dataloader):
inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 2. Pass inputs through the model to get predictions
outputs = model(inputs)
# 3. Calculate the cross-entropy loss between predictions and labels
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# 4. Compute the backward pass based on the loss
loss.backward()
# 5. Update model parameters using the optimizer
optimizer.step()
print('Epoch [{}/{}], Iteration [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, num_epochs, iter + 1, len(train_dataloader),
loss.item()))
# 6. Log the loss with SwanLab every 20 iterations
if iter % 20 == 0:
swanlab.log({"train/loss": loss.item()})
def test(model, device, val_dataloader, epoch):
model.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
# 1. Loop through val_dataloader, fetching images and labels in batches
for inputs, labels in val_dataloader:
inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
# 2. Pass inputs through the model to get predictions
outputs = model(inputs)
# 3. Get the predicted digits
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
# 4. Calculate the number of correct predictions
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
# 5. Get the final test accuracy
accuracy = correct / total
# 6. Log the accuracy with SwanLab
swanlab.log({"val/accuracy": accuracy}, step=epoch)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Check if mps is supported
try:
use_mps = torch.backends.mps.is_available()
except AttributeError:
use_mps = False
# Check if cuda is supported
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda"
elif use_mps:
device = "mps"
else:
device = "cpu"
# Initialize swanlab
run = swanlab.init(
project="MNIST-example",
experiment_name="PlainCNN",
config={
"model": "ResNet18",
"optim": "Adam",
"lr": 1e-4,
"batch_size": 256,
"num_epochs": 10,
"device": device,
},
)
# Set up MNIST training and validation sets
dataset = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True, download=True, transform=ToTensor())
train_dataset, val_dataset = utils.data.random_split(dataset, [55000, 5000])
train_dataloader = utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=run.config.batch_size, shuffle=True)
val_dataloader = utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=False)
# (Optional) Take a look at the first 16 images in the dataset
log_images(train_dataloader, 16)
# Initialize the model
model = ConvNet()
model.to(torch.device(device))
# Print the model
print(model)
# Define the loss function and optimizer
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=run.config.lr)
# Start training and testing loop
for epoch in range(1, run.config.num_epochs+1):
swanlab.log({"train/epoch": epoch}, step=epoch)
train(model, device, train_dataloader, optimizer, criterion, epoch, run.config.num_epochs)
if epoch % 2 == 0:
test(model, device, val_dataloader, epoch)
# Save the model
# Automatically create a checkpoint folder if it doesn't exist
if not os.path.exists("checkpoint"):
os.makedirs("checkpoint")
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'checkpoint/latest_checkpoint.pth')Demonstration of Results