FashionMNIST
INFO
Image Classification, Machine Learning Introduction, Grayscale Images
Overview
FashionMNIST is a widely used image dataset for testing machine learning algorithms, particularly in the field of image recognition. It was released by Zalando and is designed to replace the traditional MNIST dataset, which primarily contains images of handwritten digits. The purpose of FashionMNIST is to provide a slightly more challenging problem while maintaining the same image size (28x28 pixels) and structure (60,000 images for the training set and 10,000 images for the test set) as the original MNIST dataset.

FashionMNIST contains grayscale images of clothing and footwear items from 10 categories. These categories include:
- T-shirt/top
- Trouser
- Pullover
- Dress
- Coat
- Sandal
- Shirt
- Sneaker
- Bag
- Ankle boot
Each category has an equal number of images, making this dataset a balanced dataset. The simplicity and standardized size of these images make FashionMNIST an ideal choice for entry-level tasks in computer vision and machine learning. The dataset is widely used for education and research to test the effectiveness of various image recognition methods.
This case study primarily focuses on:
- Using
pytorchto build, train, and evaluate a ResNet34 (Residual Neural Network) model. - Using
swanlabto track hyperparameters, record metrics, and visualize monitoring throughout the training cycle.
Environment Setup
This case study is based on Python>=3.8. Please ensure Python is installed on your computer. Environment dependencies:
torch
torchvision
swanlabQuick installation command:
pip install torch torchvision swanlabComplete Code
import os
import random
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn, optim, utils
from torchvision.datasets import FashionMNIST
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor, Compose, Resize, Lambda
import swanlab
def set_seed(seed=42):
"""设置所有随机种子以确保可重复性"""
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
# 设置CUDA的随机种子
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
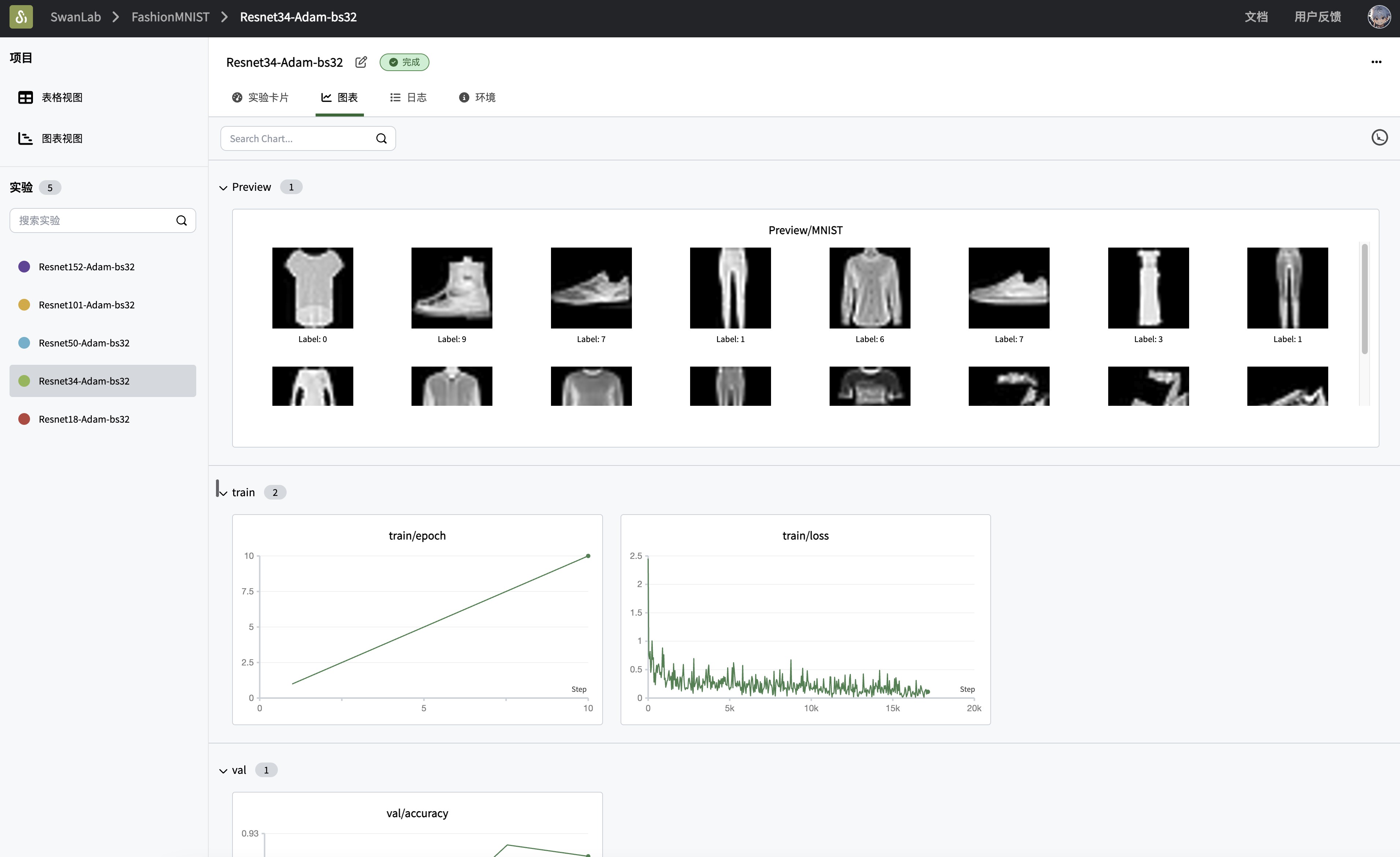
# 捕获并可视化前20张图像
def log_images(loader, num_images=16):
images_logged = 0
logged_images = []
for images, labels in loader:
# images: batch of images, labels: batch of labels
for i in range(images.shape[0]):
if images_logged < num_images:
# 使用swanlab.Image将图像转换为wandb可视化格式
logged_images.append(swanlab.Image(images[i], caption=f"Label: {labels[i]}", size=(128, 128)))
images_logged += 1
else:
break
if images_logged >= num_images:
break
swanlab.log({"Preview/FashionMNIST": logged_images})
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 设置随机种子
set_seed(42)
# 设置device
try:
use_mps = torch.backends.mps.is_available()
except AttributeError:
use_mps = False
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = "cuda"
elif use_mps:
device = "mps"
else:
device = "cpu"
# 初始化swanlab
run = swanlab.init(
project="FashionMNIST",
experiment_name="resnet50",
config={
"model": "Resnet50",
"optim": "Adam",
"lr": 1e-4,
"batch_size": 32,
"num_epochs": 10,
"train_dataset_num": 55000,
"val_dataset_num": 5000,
"device": device,
"num_classes": 10,
},
)
# 定义转换:调整大小并转换为3通道
transform = Compose([
ToTensor(),
Resize((224, 224), antialias=True), # ResNet期望224x224的输入
Lambda(lambda x: x.repeat(3, 1, 1)) # 将单通道转换为3通道
])
# 设置训练集、验证集和测试集
dataset = FashionMNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
train_dataset, val_dataset = utils.data.random_split(
dataset, [run.config.train_dataset_num, run.config.val_dataset_num]
)
train_loader = utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=run.config.batch_size, shuffle=True)
val_loader = utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
# 初始化模型、损失函数和优化器
if run.config.model == "Resnet18":
from torchvision.models import resnet18
model = resnet18(pretrained=True)
model.fc = nn.Linear(model.fc.in_features, run.config.num_classes)
elif run.config.model == "Resnet34":
from torchvision.models import resnet34
model = resnet34(pretrained=True)
model.fc = nn.Linear(model.fc.in_features, run.config.num_classes)
elif run.config.model == "Resnet50":
from torchvision.models import resnet50
model = resnet50(pretrained=True)
model.fc = nn.Linear(model.fc.in_features, run.config.num_classes)
elif run.config.model == "Resnet101":
from torchvision.models import resnet101
model = resnet101(pretrained=True)
model.fc = nn.Linear(model.fc.in_features, run.config.num_classes)
elif run.config.model == "Resnet152":
from torchvision.models import resnet152
model = resnet152(pretrained=True)
model.fc = nn.Linear(model.fc.in_features, run.config.num_classes)
model.to(torch.device(device))
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=run.config.lr)
# (可选)看一下数据集的前8张图像
log_images(train_loader, 8)
# 开始训练
for epoch in range(1, run.config.num_epochs+1):
swanlab.log({"train/epoch": epoch}, step=epoch)
model.train() # 确保模型处于训练模式
train_correct = 0
train_total = 0
# 训练循环
for iter, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
x, y = batch
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(x)
loss = criterion(output, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 计算训练准确率
_, predicted = torch.max(output, 1)
train_total += y.size(0)
train_correct += (predicted == y).sum().item()
if iter % 40 == 0:
print(
f"Epoch [{epoch}/{run.config.num_epochs}], Iteration [{iter + 1}/{len(train_loader)}], Loss: {loss.item()}"
)
swanlab.log({"train/loss": loss.item()}, step=(epoch - 1) * len(train_loader) + iter)
# 记录每个epoch的训练准确率
train_accuracy = train_correct / train_total
swanlab.log({"train/acc": train_accuracy}, step=(epoch - 1) * len(train_loader) + iter)
#
model.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
val_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in val_loader:
x, y = batch
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
output = model(x)
# 计算验证损失
loss = criterion(output, y)
val_loss += loss.item()
# 计算验证准确率
_, predicted = torch.max(output, 1)
total += y.size(0)
correct += (predicted == y).sum().item()
accuracy = correct / total
avg_val_loss = val_loss / len(val_loader)
swanlab.log({
"val/acc": accuracy,
"val/loss": avg_val_loss,
}, step=(epoch - 1) * len(train_loader) + iter)Switching to Other ResNet Models
The above code supports switching to the following ResNet models:
- ResNet18
- ResNet34
- ResNet50
- ResNet101
- ResNet152
Switching is very simple; just modify the model parameter in the config to the corresponding model name. For example, to switch to ResNet50:
# Initialize swanlab
run = swanlab.init(
...
config={
"model": "Resnet50",
...
},
)- How does
configwork? 👉 Set Experiment Configuration
Demonstration of Results