Keras
Keras is a high-level neural network API written in Python, originally created by François Chollet and merged into TensorFlow in 2017, but still usable as a standalone framework. It is an open-source deep learning framework that runs on top of deep learning backends such as TensorFlow, Theano, or Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK).

You can use Keras to quickly train models while using SwanLab for experiment tracking and visualization.
1. Import SwanLabLogger
python
from swanlab.integration.keras import SwanLabLogger2. Integrate with model.fit
First, initialize SwanLab:
python
swanlab.init(
project="keras_mnist",
experiment_name="mnist_example",
description="Keras MNIST Example"
)Then, add SwanLabLogger to the callbacks parameter in model.fit to complete the integration:
python
model.fit(..., callbacks=[SwanLabLogger()])3. Example - MNIST
python
from swanlab.integration.keras import SwanLabLogger
import tensorflow as tf
import swanlab
# Initialize SwanLab
swanlab.init(
project="keras_mnist",
experiment_name="mnist_example",
description="Keras MNIST Example"
)
# Load and preprocess MNIST data
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype('float32') / 255.0
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype('float32') / 255.0
# Build a simple CNN model
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
# Compile the model
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
# Train the model with SwanLabLogger
model.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
epochs=5,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
callbacks=[SwanLabLogger()]
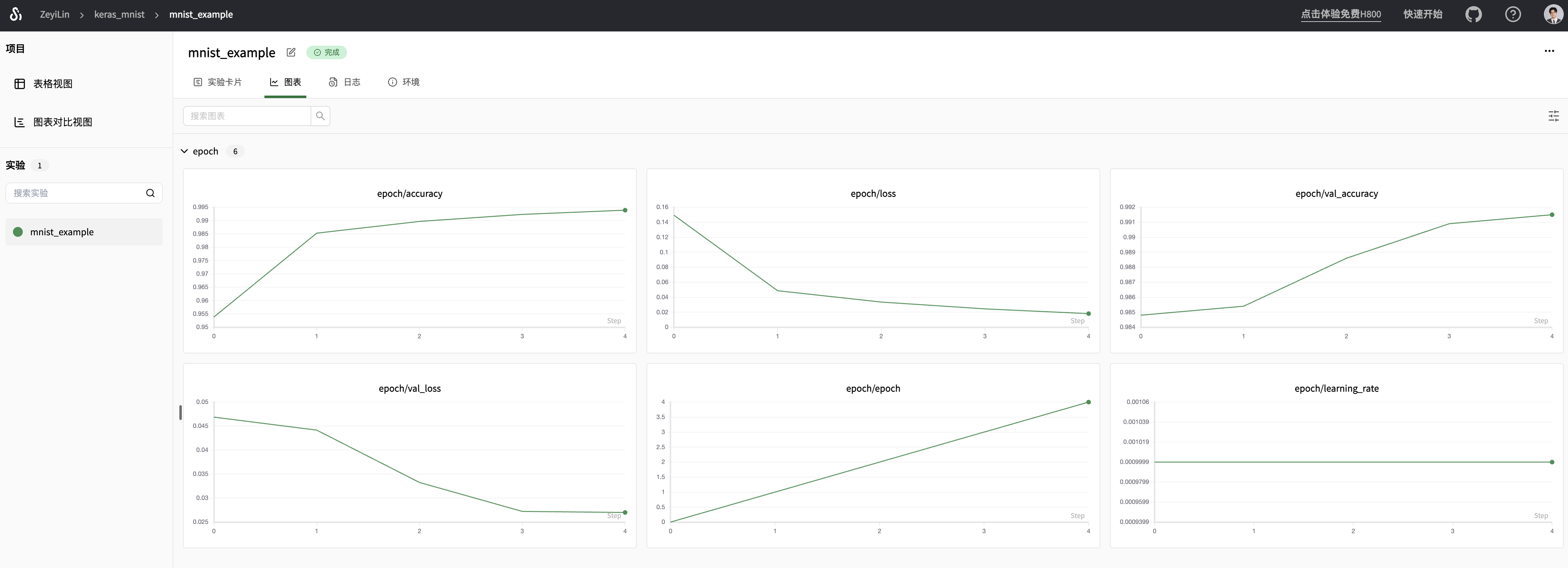
)Effect demonstration: