Weights & Biases
Weights & Biases (Wandb) is a platform for experiment tracking, model optimization, and collaboration in machine learning and deep learning projects. W&B provides powerful tools to log and visualize experimental results, helping data scientists and researchers better manage and share their work.
Synchronization Tutorials for Other Tools
You can sync projects from Wandb to SwanLab in three ways:
- Real-time Syncing: If your current project uses wandb for experiment tracking, you can use the
swanlab.sync_wandb()command to simultaneously log metrics to SwanLab while running your training script. - Convert existing projects from the wandb website: If you want to copy projects from the wandb server (wandb.ai or privately deployed wandb) to SwanLab, you can use
swanlab convertto transform existing Wandb projects into SwanLab projects. - Convert existing projects from local wandb log files: If you want to upload local wandb log files to SwanLab, you can use
swanlab convertto transform local wandb log files into SwanLab projects.
INFO
The current version only supports converting scalar charts.
1. Live Synchronization
1.1 Add the sync_wandb Command
Add the swanlab.sync_wandb() command anywhere in your code before wandb.init() to synchronize Wandb metrics to SwanLab during training.
import swanlab
swanlab.sync_wandb()
...
wandb.init()With this implementation, wandb.init() will simultaneously initialize SwanLab, using the same project, name, and config parameters from wandb.init(). Therefore, you don’t need to manually initialize SwanLab.
INFO
sync_wandb supports two parameters:
mode: SwanLab logging mode, supportingcloud,local, anddisabled.wandb_run: If set to False, data will not be uploaded to Wandb (equivalent towandb.init(mode="offline")).
1.2 Alternative Implementation
Another approach is to manually initialize SwanLab first before running Wandb code.
import swanlab
swanlab.init(...)
swanlab.sync_wandb()
...
wandb.init()In this implementation, the project name, experiment name, and configuration will follow the project, experiment_name, and config parameters from swanlab.init(). Subsequent wandb.init() parameters for project and name will be ignored, while config will update swanlab.config.
1.3 Test Code
import wandb
import random
import swanlab
swanlab.sync_wandb()
# swanlab.init(project="sync_wandb")
wandb.init(
project="test",
config={"a": 1, "b": 2},
name="test",
)
epochs = 10
offset = random.random() / 5
for epoch in range(2, epochs):
acc = 1 - 2 ** -epoch - random.random() / epoch - offset
loss = 2 ** -epoch + random.random() / epoch + offset
wandb.log({"acc": acc, "loss": loss})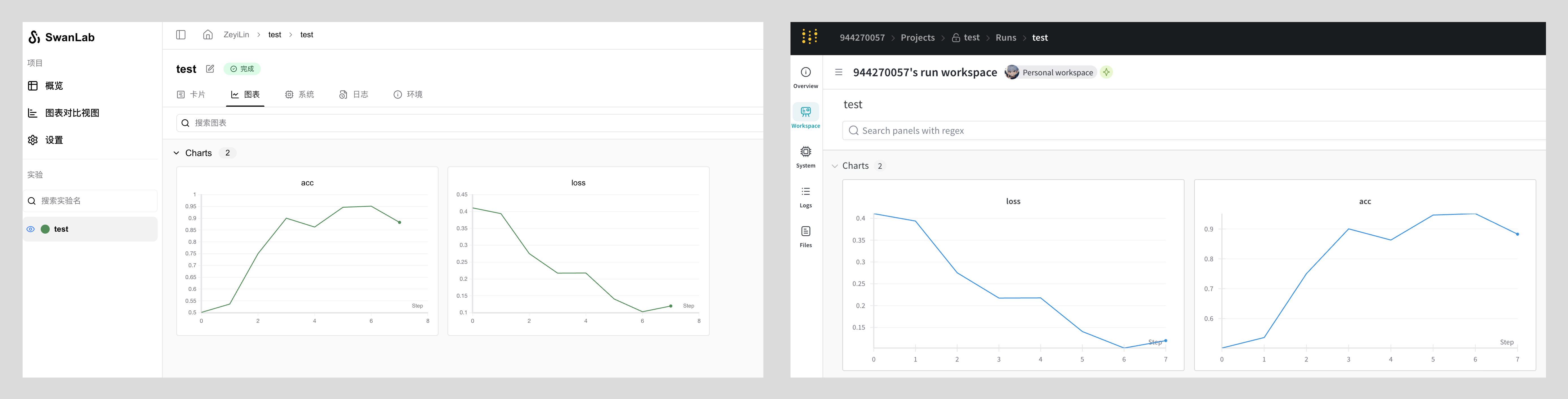
2. Convert Existing Projects
2.1 Locate Your project, entity, and runid on wandb.ai
The conversion requires project, entity, and optionally runid.
Locations of project and entity: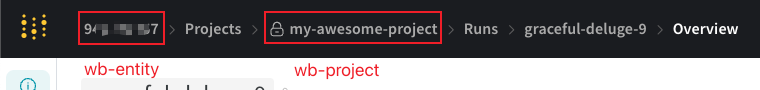
Location of runid: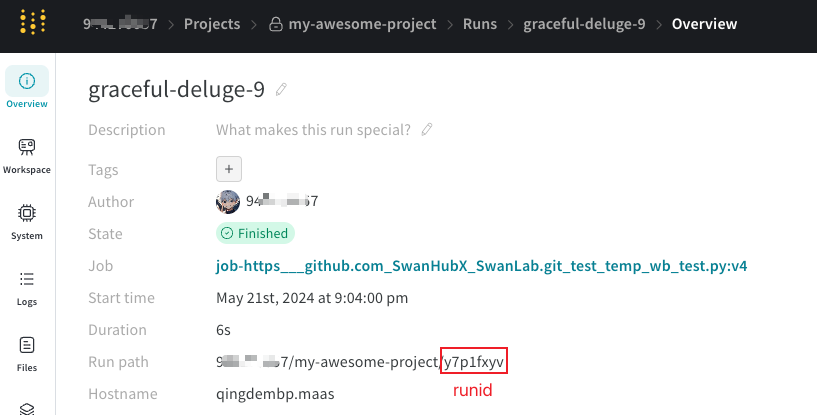
2.2 Method 1: Command-Line Conversion
First, ensure you are logged into Wandb and have access to the target project.
Conversion command:
swanlab convert -t wandb --wb-project [WANDB_PROJECT_NAME] --wb-entity [WANDB_ENTITY]Supported parameters:
-t: Conversion type (wandbortensorboard).-p: SwanLab project name.-w: SwanLab workspace name.--mode: (str) Logging mode (default:"cloud"), options:["cloud", "local", "offline", "disabled"].-l: Log directory path.--wb-project: Wandb project name to convert.--wb-entity: Wandb entity (username/team) where the project resides.--wb-runid: Wandb Run ID (specific experiment under the project).
If --wb-runid is omitted, all Runs under the project will be converted. If specified, only the selected Run will be converted.
Asynchronous Conversion (Download Data Locally First, Then Upload to SwanLab)
- Download data locally:
swanlab convert --mode 'offline' -t wandb --wb-project [WANDB_PROJECT_NAME] --wb-entity [WANDB_ENTITY]- Upload to SwanLab:
swanlab sync [LOG_DIRECTORY_PATH]2.3 Method 2: In-Code Conversion
from swanlab.converter import WandbConverter
wb_converter = WandbConverter()
# wb_runid is optional
wb_converter.run(wb_project="WANDB_PROJECT_NAME", wb_entity="WANDB_USERNAME")This achieves the same result as command-line conversion.
WandbConverter parameters:
project: SwanLab project name.workspace: SwanLab workspace name.mode: (str) Logging mode (default:"cloud"), options:["cloud", "local", "offline", "disabled"].logdir: Log directory path.
WandbConverter.run parameters:
wb_project: Wandb project name.wb_entity: Wandb entity (username/team).wb_runid: Wandb Run ID (specific experiment).
Asynchronous Conversion (Download Data Locally First, Then Upload to SwanLab)
- Download data locally:
from swanlab.converter import WandbConverter
wb_converter = WandbConverter(mode="offline")
# wb_runid is optional
wb_converter.run(wb_project="WANDB_PROJECT_NAME", wb_entity="WANDB_USERNAME")- Upload to SwanLab:
swanlab sync [LOG_DIRECTORY_PATH]3 Converting wandb Log Files
3.1 Locating Your Log Files
wandb log files refer to the folders that wandb automatically creates in the training directory (default is the wandb directory) during experiment tracking, as shown below:

3.2 Method 1: Command Line Conversion
The conversion command is:
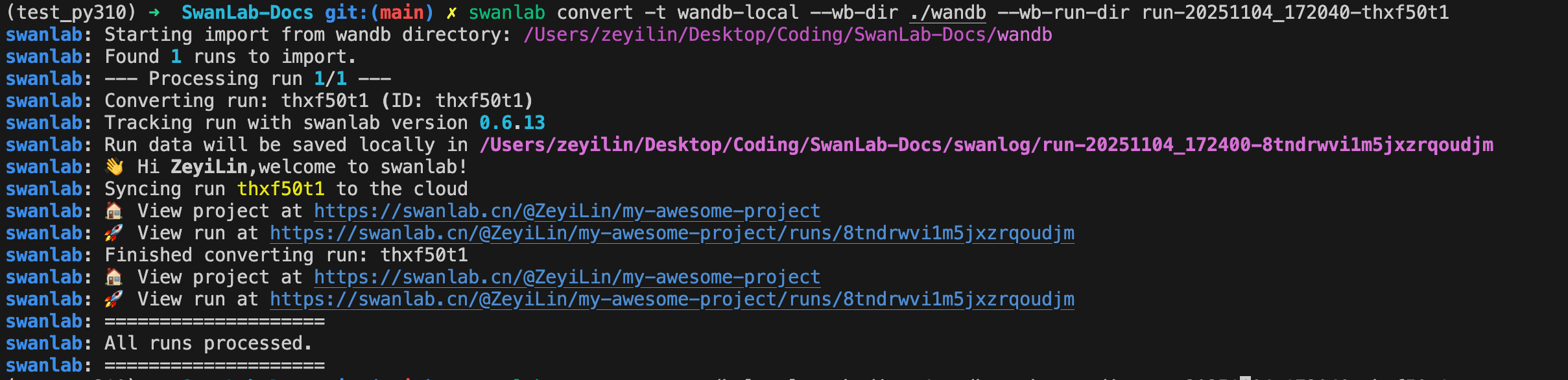
swanlab convert -t wandb-local --wb-dir [WANDB_LOG_DIR] --wb-run-dir [WANDB_RUN_DIR]Supported parameters are as follows:
-t: Conversion type. Options: wandb, tensorboard, mlflow, wandb-local.-p: SwanLab project name.-w: SwanLab workspace name.--mode: (str) Selection mode. Default is "cloud". Options: ["cloud", "local", "offline", "disabled"]-l: logdir path.--wb-dir: The wandb log directory to be converted.--wb-run-dir: The specific wandb run's directory name. If this parameter is omitted, all runs within the wb-dir will be uploaded.
Example:
3.3 Method 2: Code Conversion
from swanlab.converter import WandbLocalConverter
wb_converter = WandbLocalConverter()
# wb_runid is optional
wb_converter.run(root_wandb_dir="WANDB_DIR", wandb_run_dir="WANDB_RUN_DIR")Parameters supported by WandbLocalConverter:
project: SwanLab project name.workspace: SwanLab workspace name.mode: (str) Selection mode. Default is "cloud". Options: ["cloud", "local", "offline", "disabled"]logdir: logdir path.
Parameters supported by WandbLocalConverter.run:
root_wandb_dir: The path to the wandb log file directory.wandb_run_dir: The path to the wandb run directory.