PaddleNLP
PaddleNLP is a large language model (LLM) development toolkit based on the PaddlePaddle deep learning framework. It supports efficient large-scale model training, lossless compression, and high-performance inference on various hardware. PaddleNLP is designed for simplicity and极致 performance, empowering developers to achieve efficient industrial-level applications of large models.

You can use PaddleNLP for rapid model training while leveraging SwanLab for experiment tracking and visualization.
1. Integrating SwanLabCallback
from swanlab.integration.paddlenlp import SwanLabCallbackThe SwanLabCallback is a logging class tailored for PaddleNLP.
Configurable parameters for SwanLabCallback include:
project,experiment_name,description, and other parameters consistent withswanlab.init, used for initializing the SwanLab project.- Alternatively, you can create a project externally via
swanlab.init, and the integration will log experiments to the externally created project.
2. Passing to Trainer
from swanlab.integration.paddlenlp import SwanLabCallback
from paddlenlp.trainer import TrainingArguments, Trainer
...
# Instantiate SwanLabCallback
swanlab_callback = SwanLabCallback(project="paddlenlp-demo")
trainer = Trainer(
...
# Pass the callback via the `callbacks` parameter
callbacks=[swanlab_callback],
)
trainer.train()3. Complete Example Code
Requires connectivity to the HuggingFace server to download the dataset.
"""
Tested with:
pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==3.0.0 -i https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/packages/stable/cu126/
pip install paddlenlp==3.0.0b4
"""
from paddlenlp.trl import SFTConfig, SFTTrainer
from datasets import load_dataset
from swanlab.integration.paddlenlp import SwanLabCallback
dataset = load_dataset("ZHUI/alpaca_demo", split="train")
training_args = SFTConfig(
output_dir="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-SFT",
device="gpu",
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
logging_steps=20
)
swanlab_callback = SwanLabCallback(
project="Qwen2.5-0.5B-SFT-paddlenlp",
experiment_name="Qwen2.5-0.5B",
)
trainer = SFTTrainer(
args=training_args,
model="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct",
train_dataset=dataset,
callbacks=[swanlab_callback],
)
trainer.train()4. GUI Demonstration
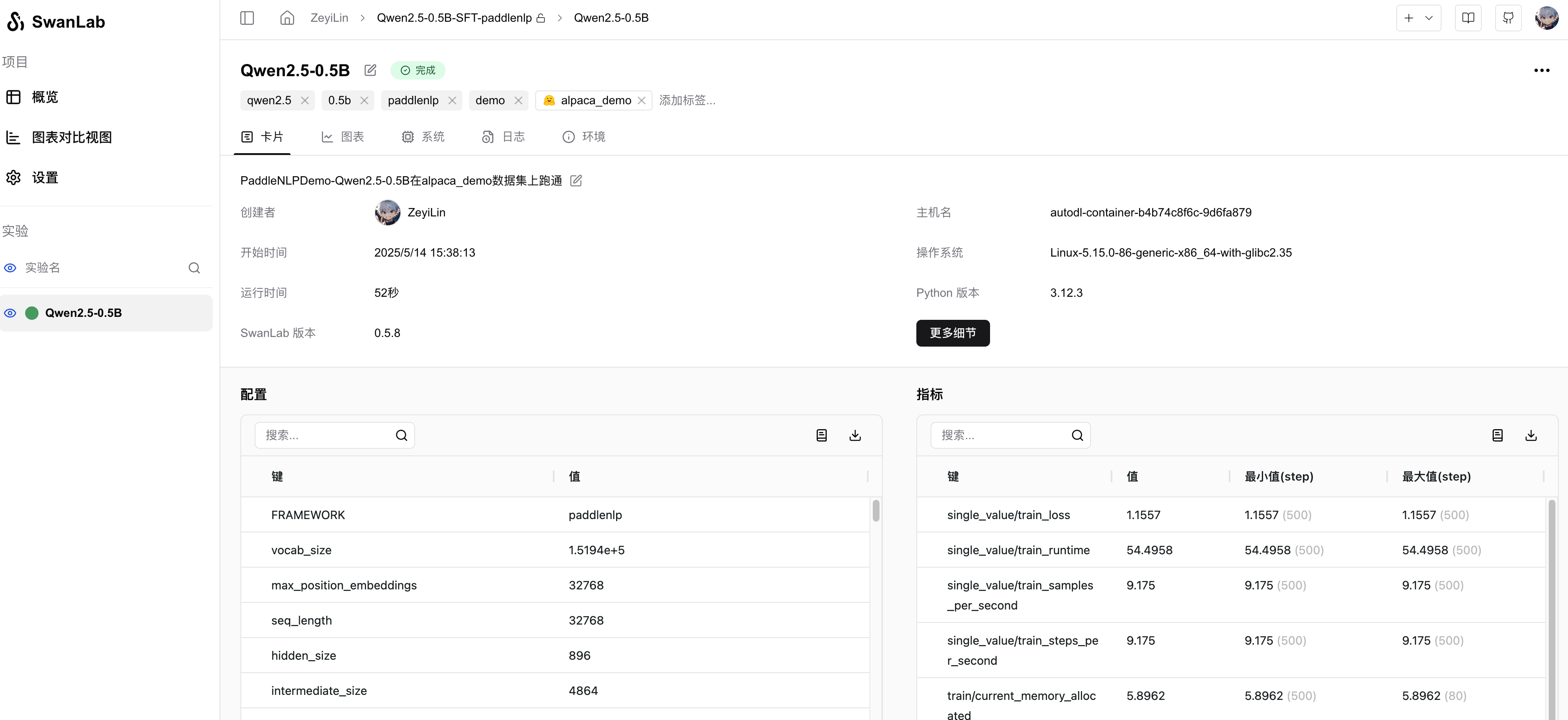
Automatically Logged Hyperparameters:
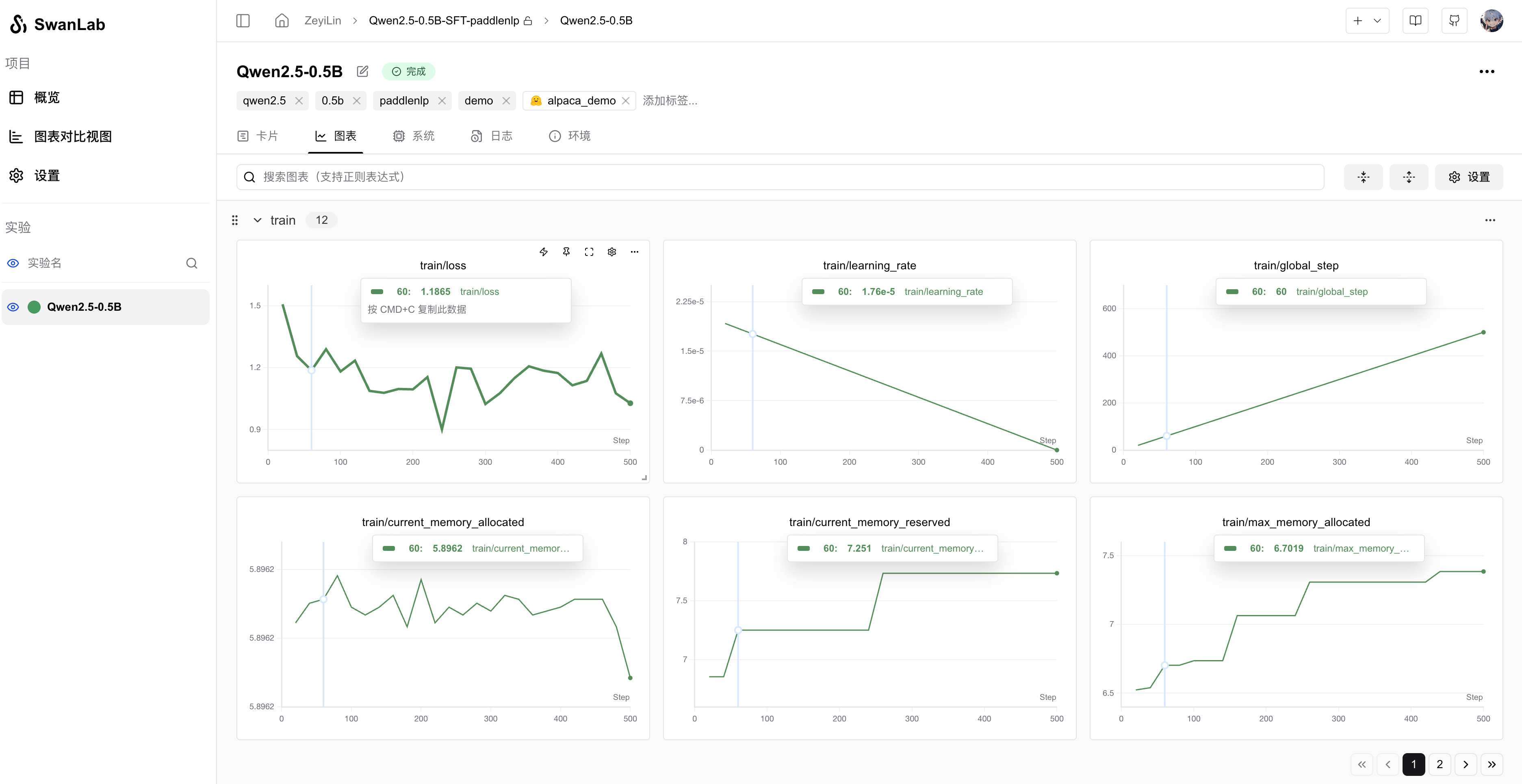
Metrics Logging:
5. Extension: Adding More Callbacks
Imagine a scenario where you want the model to infer test samples at the end of each epoch and log the results with SwanLab. You can create a new class inheriting from SwanLabCallback and extend or override lifecycle functions. For example:
class NLPSwanLabCallback(SwanLabCallback):
def on_epoch_end(self, args, state, control, **kwargs):
test_text_list = ["example1", "example2"]
log_text_list = []
for text in test_text_list:
result = model(text)
log_text_list.append(swanlab.Text(result))
swanlab.log({"Prediction": test_text_list}, step=state.global_step)The above is a new callback class for NLP tasks, extending the on_epoch_end function, which executes at the end of each epoch during transformers training.