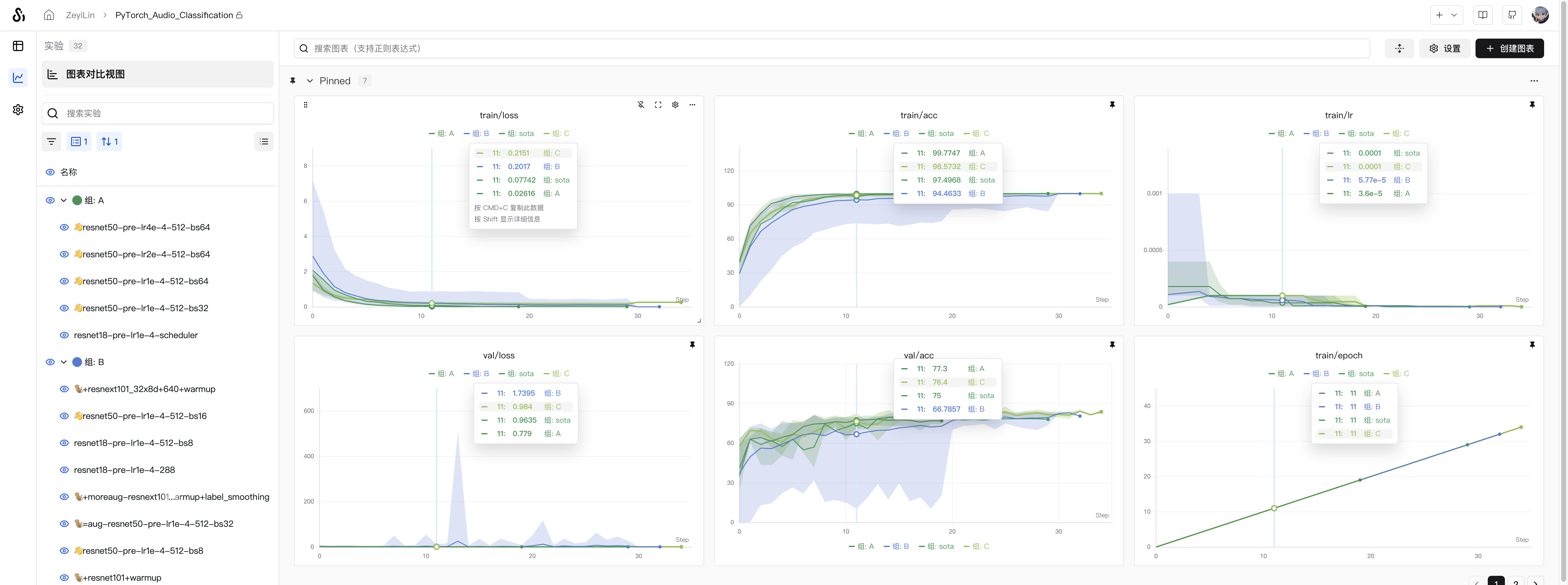
Grouping Experiments
Group multiple training and evaluation runs into larger experiments.
Pass the group parameter to swanlab.init to set the group for new experiments.
Use Cases
- Distributed training: Use grouping when experiments are split into different parts with separate training and evaluation scripts that should be viewed as a single whole.
- Multi-process experiments: Combine multiple smaller processes into one experiment.
- K-fold cross-validation: Combine experiments with different random seeds into a complete experiment for comparison.
Setting Group
1. Set Group in Code
Pass the group parameter when initializing the experiment to assign it to the corresponding experiment group. The job_type parameter can be used to identify the experiment's task type (optional):
import swanlab
swanlab.init(
experiment="my_experiment",
group="experiment_1", # Related experiments use the same group name
job_type="demo", # Training task
)2. Set Group via Environment Variable
Use the SWANLAB_GROUP environment variable to specify the experiment's group:
import os
import swanlab
# Use swan's built-in ID generator to create a unique group name
os.environ["SWANLAB_GROUP"] = "experiment-1"
swanlab.init(experiment="my_experiment")Use the
SWANLAB_JOB_TYPEenvironment variable to specify the experiment's task type.
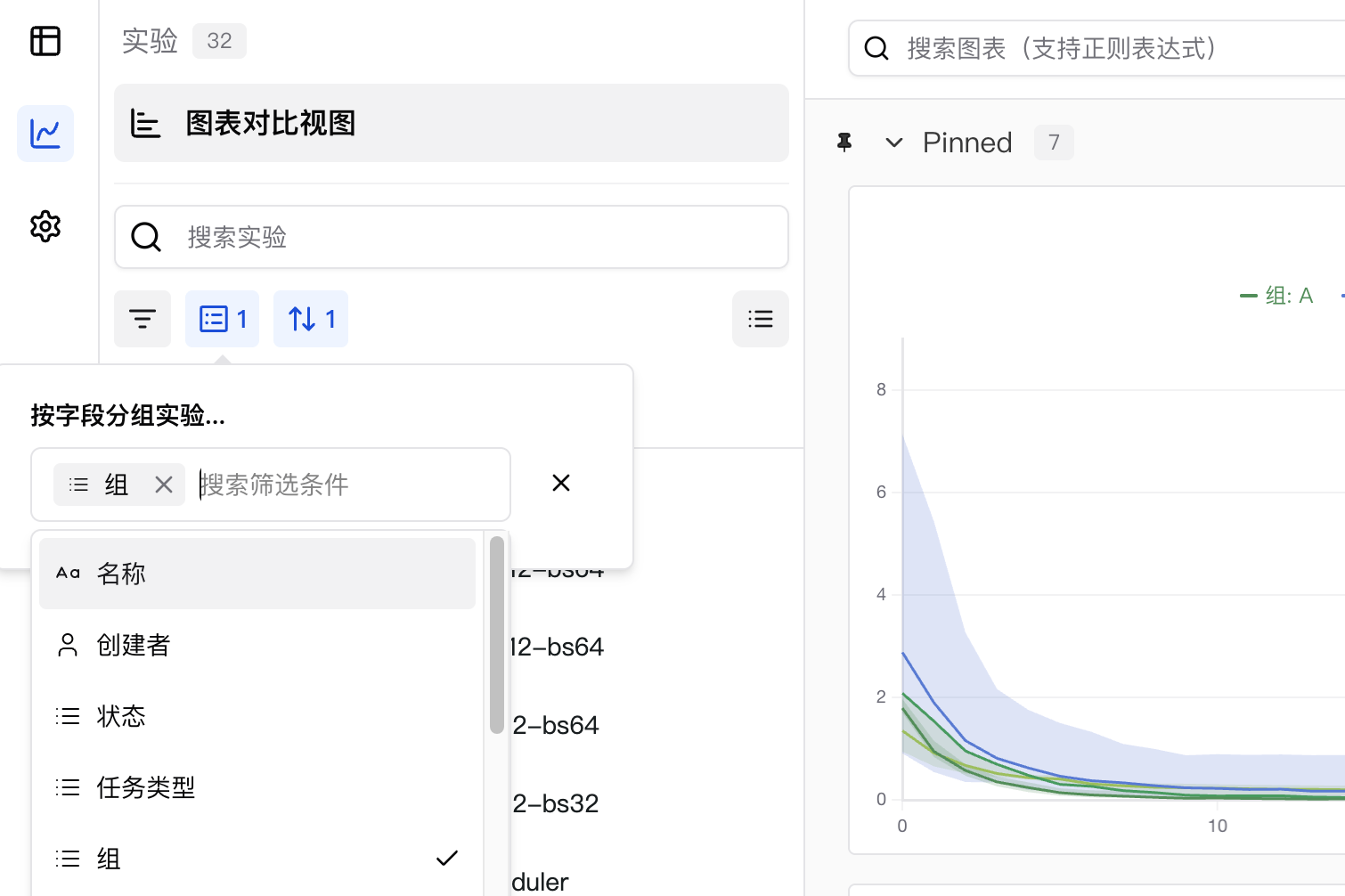
3. Set Group in UI
SwanLab supports dynamic grouping of experiments by any column, including hidden columns. For example, if you use swanlab.config to log hyperparameters like batch size or learning rate, you can dynamically group by these hyperparameters directly in the web application.
Note: The Group column in the experiment list is hidden by default.
To group experiments by one or more columns:
- Click the Group button.
- Click the name of one or more columns.