Webhook Usage Guide
SwanLab webhook operates on a per-experiment basis and triggers the webhook logic simultaneously when an experiment is created.
Usage
Set the SwanLab WebHook via an environment variable:
bash
export SWANLAB_WEBHOOK='http://127.0.0.1/webhook'
# Optional, if you need to pass additional information, you can set this environment variable
export SWANLAB_WEBHOOK_VALUE='Hello World!'After setting this up, SwanLab will send a POST callback when the experiment starts (i.e., when swanlab.init() is called).
Callback Structure
The webhook sends callbacks using the POST method. The callback structure is described below using TypeScript type notation:
ts
interface SwanLabInfo {
// SwanLab version number
version: string
// SwanLab running mode
mode: 'cloud' | 'local' | 'offline' | 'disabled'
// Log storage path
swanlog_dir: string
// Cloud experiment URL
exp_url: string
}
// Webhook callback structure
interface Body{
value: string
swanlab: SwanLabInfo
}Minimal Test
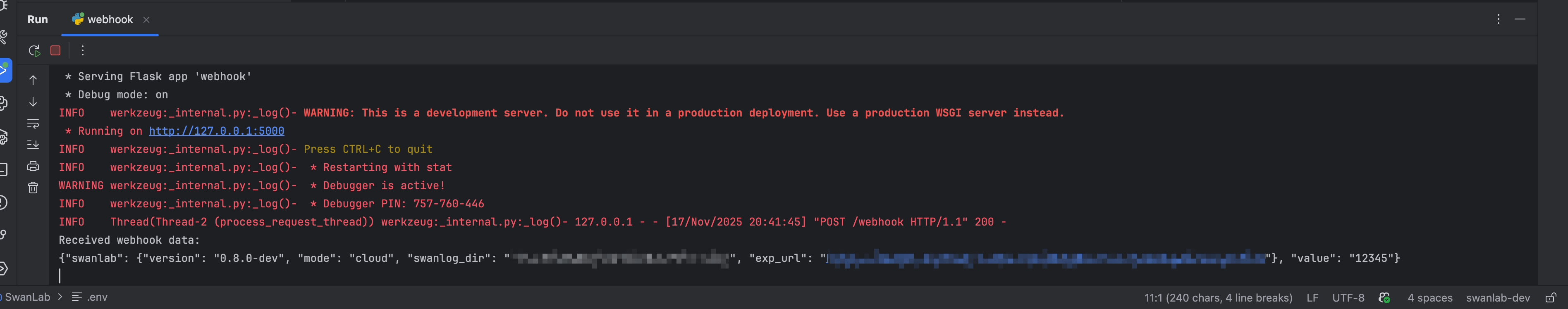
Here is a minimal test code using the Flask framework:
python
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/webhook', methods=['POST'])
def webhook():
# Get request body data
data = request.get_data(as_text=True) # Get data as text
print("Received webhook data:")
print(data)
return "Webhook received successfully!", 200
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='127.0.0.1', port=5000, debug=True)After running the service, execute the following script in a new terminal:
bash
export SWANLAB_WEBHOOK='http://127.0.0.1:5000/webhook'
export SWANLAB_WEBHOOK_VALUE='12345'
export SWANLAB_API_HOST='Your backend API HOST'
export SWANLAB_WEB_HOST='Your backend WEB HOST'
python -c "import swanlab;swanlab.init()"You will receive content similar to the following: